Helm is the package manager for Kubernetes, you can think it as yum/apt/homebrew. It contains two parts: Server (tiller) and Client (helm). helm client can be installed on Linux/Mac/Windows, the package can be found here. Helm manages the Kubernetes charts which are pre-configured Kubernetes resources. In the following example, I will show you how to … Continue reading Use helm in Kubernetes
Use AWS EFS for Kubernetes
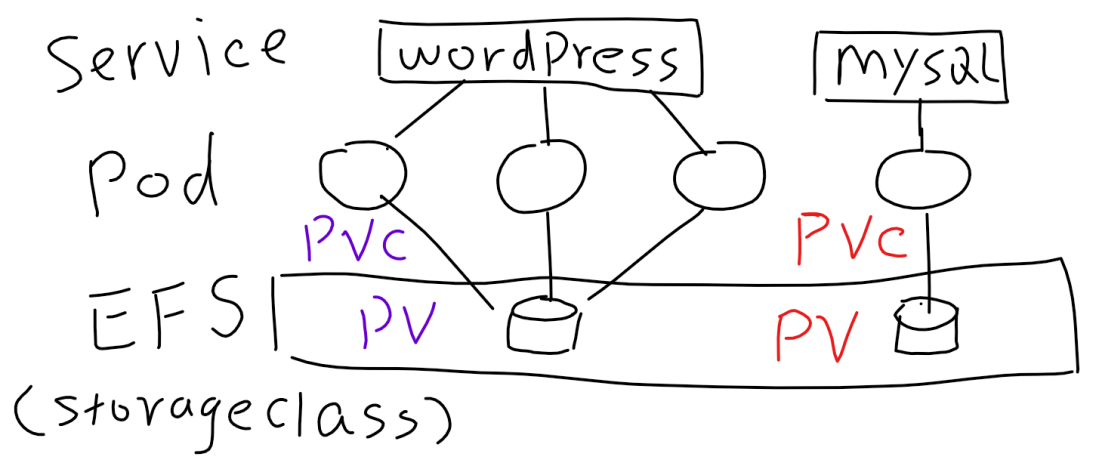
Before introducing how to use AWS EFS for Kubernetes, let me recap some terms of Persistent Volumes. PV (Persistent Volume): PV is a piece of storage, it can be NFS, iSCSI, EBS, EFS... The purpose of having PV is to decouple the storage from pod's lifecycle. PVC (Persistent Volume Claim): PVC provides the method for … Continue reading Use AWS EFS for Kubernetes
Understanding Ingress in Kubernetes
Simply speaking ingress is a collection of routing rules, and ingress controller is the component that implements those rules in Kubernetes cluster. It is not available in any Kubernetes releases prior to 1.1. I guess it is the reason that why OpenShift developed Router. This is a not so nice diagram, but I think it … Continue reading Understanding Ingress in Kubernetes
High Availability in Kubernetes cluster built by kops
In my previous post, I have shown you how to create a Kubernetes cluster on AWS with kops. And this article I will dig deeper in to the Kubernetes HA (High-Availability) that is built by kops. Here is a diagram that shows you the high level HA design of the cluster that I built. Here … Continue reading High Availability in Kubernetes cluster built by kops
Install Kubernetes on AWS with kops
It was year 2015 when I first time installed Kubernetes. Back then, installing Kubernetes is not a simple task like what it is Today. Nowadays, there are a few handy tools that you can choose, eg. kops, heptio. Additionally, you can also choose managed Kubernetes, e.g GKE, AKS, EKS and more. I recently used kops … Continue reading Install Kubernetes on AWS with kops